Business
October 6, 2025
Vietnam’s GDP Growth in Q3 2025 Hits 8.23%: What Drives the Surge and What Lies Ahead?
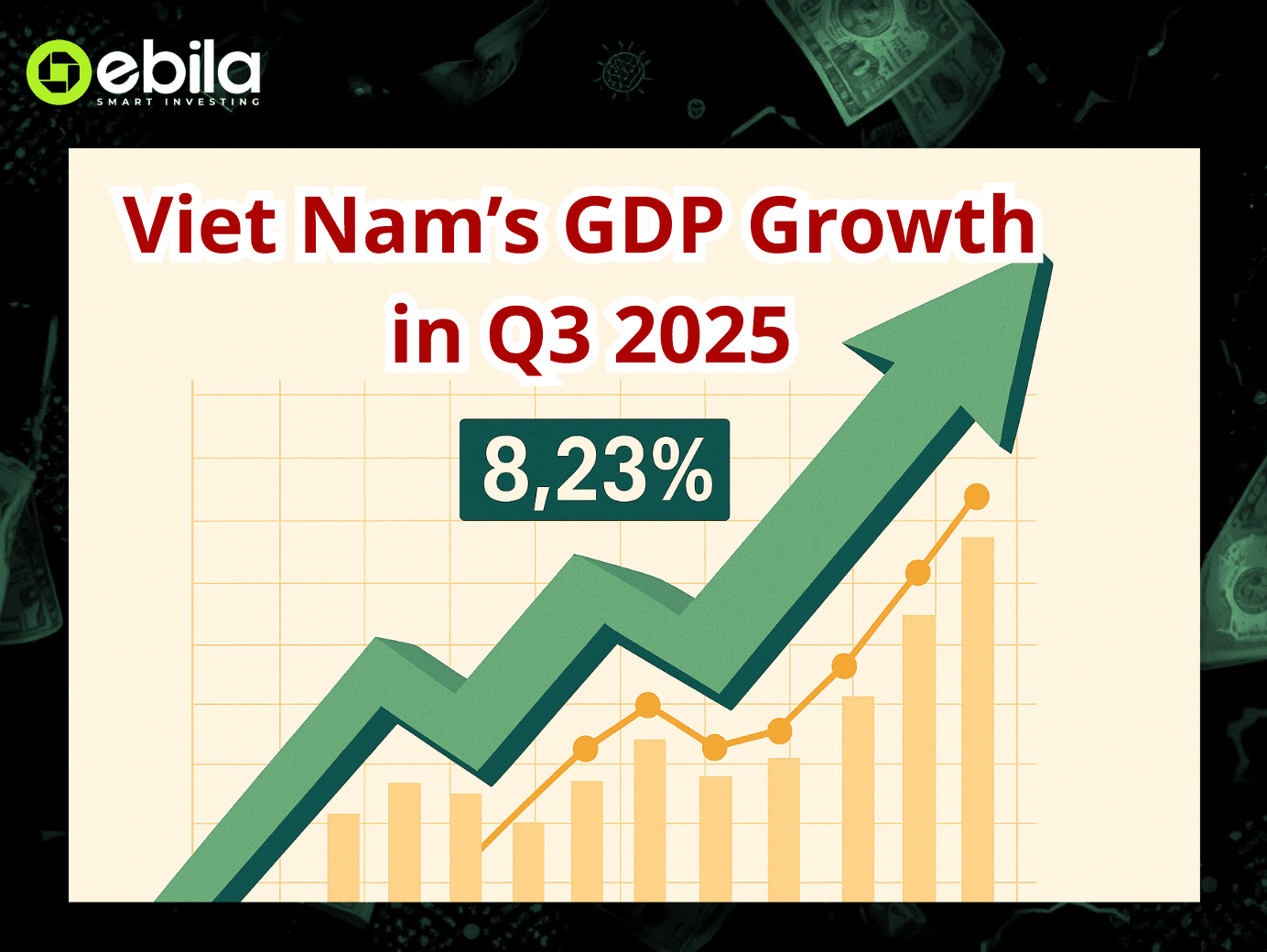
In the third quarter of 2025, Vietnam’s economy expanded by 8.23% year-on-year, the second-highest growth in over a decade (trailing only the post-Covid rebound in 2022). Cumulatively, GDP for the first nine months rose 7.85%, setting a solid foundation for the government’s ambitious 8–8.5% full-year target.
The 8.23% figure, released on October 6, signals a broad-based recovery across manufacturing, services, and domestic consumption.
Overview: Not Just Impressive—But Solid
GDP Q3/2025: +8.23% y/y; First 9 months: +7.85% — both among the strongest growth rates in the past 11 years (except 2022’s rebound).
Main growth drivers:
Services: +8.56%, contributing ~48.6% of total added value
Industry & construction: +9.46%, contributing ~46.4%
Agriculture–forestry–fishery: +3.74%, contributing ~5%
Inflation remained contained: September CPI rose 3.38% y/y, averaging 3.38% in the first 9 months.
Foreign trade served as a stabilizing force: exports rose 18.4% y/y in Q3 to $128.6 billion, imports +20.2% to $119.7 billion, resulting in a $8.9 billion trade surplus for the quarter and ~$16.8 billion over nine months.
These numbers confirmed by official statistics and international media—reflect a robust and credible picture of Vietnam’s economic momentum.
Why Did the Economy Accelerate by 8.23%?
Manufacturing and Processing Led the Charge
Industrial added value grew 8.55% in the first nine months, with manufacturing and processing up 9.92%—the key growth engine. This demonstrates strong FDI inflows and supply chain resilience as global firms continue to diversify production to Vietnam.
Services Boomed Thanks to Domestic Demand and Tourism
Services expanded 8.49% in the first nine months, contributing ~51.6% to GDP growth. Retail, transportation, and hospitality saw double-digit gains as consumer spending rebounded.
International arrivals surged 21.5%, reaching 15.4 million visitors.
Pro-Growth Monetary Policy
The State Bank of Vietnam maintained an accommodative stance, targeting 19–20% credit growth for the year and promoting lower lending rates to boost business activity. At the same time, it tightened supervision to prevent excessive risk-taking in real estate and speculative assets.
Export Rebound Despite Global Headwinds
Vietnam’s export performance surprised positively, sustaining strong trade surpluses even amid global uncertainties—a crucial buffer against external shocks.
Challenges Beneath the Surface
Despite the optimism, several external risks persist:
New U.S. tariffs on select Vietnamese exports took effect in August, raising cost pressures for exporters. Although trade data remains strong, prolonged tariffs could erode competitiveness.
Climate and weather disruptions—notably floods and storms—continue to threaten supply chains and agriculture.
Imported inflation risks loom as global energy prices climb, requiring careful coordination between fiscal and monetary policies to avoid asset bubbles.
Implications for Businesses and Investors
For Exporters and Manufacturers
Capitalize on the rebound in electronics, textiles, wood, and plastics, but diversify markets to mitigate tariff risks.
Review rules of origin compliance and strengthen domestic supply chains to avoid re-export accusations.
Proactively restructure finances as interest rates remain supportive but may rise again if inflation pressures return.
For Retail, Services, and Tourism
With domestic demand recovering and foreign tourists returning, firms should enhance digital transformation in marketing and operations, and elevate customer experience to capture new growth.
For Construction and Materials
Public investment disbursement and infrastructure projects continue to drive demand, but cost management and liquidity control remain critical.
For Financial Investors
Strong growth and stable inflation support earnings in consumer, retail, logistics, and banking sectors.
In export-oriented industries, focus on firms with high localization rates, diversified client bases, and strong compliance with trade rules.
Scenarios for the Remainder of 2025
Optimistic Scenario:
Exports maintain double-digit growth, domestic demand strengthens, credit expands steadily, inflation stays within 3–3.5% → GDP could reach 8.5% for the year.Baseline Scenario:
U.S. tariffs mildly affect exports, energy prices remain manageable, and supportive policies continue → GDP around 8.0–8.3%.Downside Risks:
Prolonged trade protectionism, severe climate events, or sudden shifts in global capital costs could drag growth below expectations.
The 8.23% GDP growth in Q3 2025 is not only visually impressive but structurally strong: broad-based across industries, with manufacturing and services both contributing heavily, while inflation and trade remain stable.
However, external headwinds and cyclical uncertainties call for prudent management and diversification. If momentum continues, Vietnam’s 8–8.5% full-year growth goal is within reach realistic, not just aspirational.